git 入门
git 是 Linux 之父 Linus 开发的开源的分布式版本控制系统,通常用于代码的版本控制。和 SVN 这样依赖中心服务器的版本控制系统不同的是,git 是分布式的,因此被称为分布式版本控制系统。
基本概念
- 代码仓库:一般是指正在使用 git 的项目及其所有记录版本。
- 提交:提交是 git 版本控制的最小单位,每个提交都有一个 UUID 作为区分,以及提交信息作为注释。
- HEAD:当前代码库所位于的提交。
- 分支:如果你用过别的版本控制系统,那么你一定听说过分支,你(或者你的团队)可以在不同的分支上 独立地开发多个特性,并在合适的时候将它们合并在一起。
- upstream:你的分支需要有对应的上游分支才能直接 push。
- 暂存区:已修改但未提交的代码需要先添加到暂存区才能提交。
基本命令
| git xxx 命令 | 作用 | | :----------- | :----------------------------------------------------------- | | status | 显示 repo 当前状态 | | commit | 提交代码 | | push | 推送代码 | | fetch | 拉取代码 | | merge | 合并代码 | | pull | 拉去并合并代码 | | rebase | 衍合/变基。将某次提交后的所有提交按照需要应用到指定提交上。 | | config | 设置 | | tag | 打标签 | | checkout | 检出某次提交或者某个分支 | | clone | 克隆代码库到本地 | | add | 将变动添加到暂存区 |
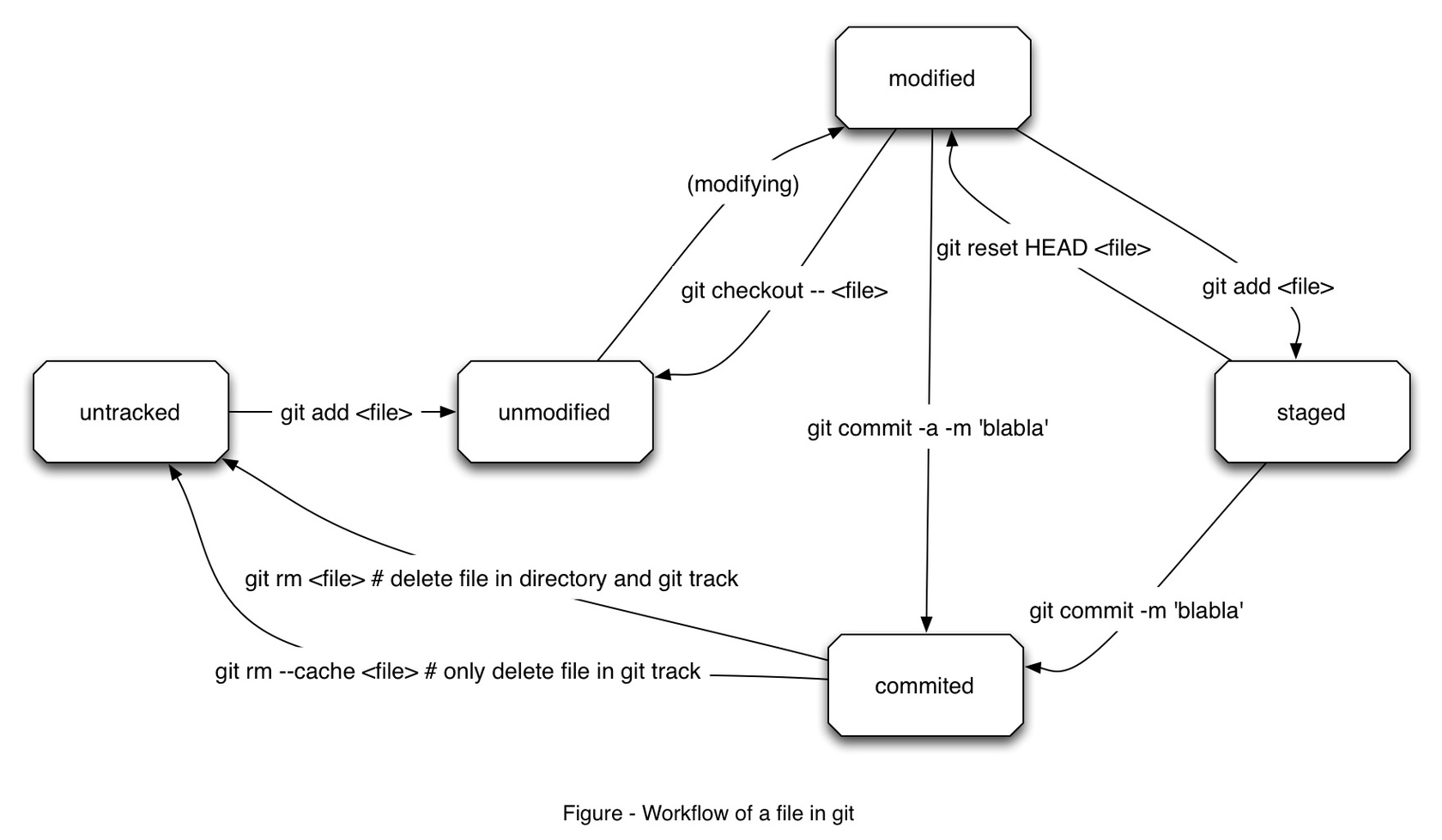
文件状态
git 对 repo 的管理以文件为对象,在使用过程中一个文件会存在以下常见状态变化:
- untracked:未添加。在仓库目录刚创建的尚未添加至 repo 的文件状态即是 untracked。也可以把已存在于 repo 中的文件从中删去,这时文件的状态也会回到了 untracked。
- unmodified:新文件添加进来后并没有对照的历史版本,状态即 unmodified。
- modified:unmodified 的文件发生修改、变动后其状态会改变为 modified。
- staged:暂存状态。通过 add 命令记录待提交的文件,文件的状态会变味暂存状态。
- commited:暂存文件提交后其状态即是 commited,当然也是 unmodified。
最简单的流程
1.从远程 clone 代码仓库:git clone https://github.com/kxxoling/blog.git
- 将本地 master 分支与远程 master 分支关联起来:
git remote add origin master - 修改代码(比如创建文件 a.txt):
touch a.txt - 将改动添加到暂存区:
git add a.txt - 提交改动:
git commit -m "添加了 a.txt - 上传到原仓库:
git push
rebase 和 cherry-pick
常用命令
添加 upstream:
git upstream add origin [git repo addr]
删除远程分支:
git push --delete [branch_name] # 缩写形式:git branch -d [branch_name]
或者:
git branch -dr [remote] [branch]
清除无用代码/文件:
git clean -f # 删除 untracked 状态的文件
git clean -fd # 删除 untracked 状态的文件和目录
git clean -nfd # 列出所有会删除的文件和目录(并不执行删除)
列出当前所有分支:
git branch --all[ --verbose] # verbose 参数可以同时显示出分支的 HEAD commit,缩写形式: git branch -av
显示文件的修改纪录和修改人信息:
git blame [filename]
发布 tag:
git push --tags
reset、revert、checkout 的区别
| 命令\作用对象 | 文件 | commit | | :------------ | :----------------------- | :--------------------------------------------------------- | | reset | 清除文件的未提交改动 | 丢弃私有分支中某次提交之后的所有提交,或者丢失未提交的改动 | | checkout | 放弃工作目录中的所有改动 | 切换分支,或者检出某个版本的文件快照 | | revert | | 将公共分支的代码强制覆盖为某个版本的代码 |
其它常用命令
撤销提交
撤销提交最简单的方式是 git add/git remove 相应文件后运行:
git commit --amend
然后会直接回到编辑提交信息的 UI。(通常是使用默认编辑器编辑 commit 信息)
或者可以一次性运行:
git commit [file1] [file2] ... -m [message]
提交并显示详细信息和 diff 信息:
git commit -v
使用一次新的 commit,替代上一次提交,如果代码没有任何新变化,则用来改写上一次 commit 的提交信息
git commit --amend -m [message]
重做上一次 commit,并包括指定文件的新变化
git commit --amend [file1] [file2] ...
折叠显示 diff 信息
我常用的方法是通过管道将 git diff 结果传递给 less,实际上 git 内置了分页(pager)的支持,
diff 的时候加上 -s 参数即可设置 less 作为 pager,全局设置命令:
git config core.pager 'less -r'
clone 特定分支
项目很大或者网络很差的时候你可能只打算 clone 其中某一个分支:
git clone REPO_URI[ TARGET_FOLDER][ -b/--branch SOME_BRANCH]
`REPO_URI` 可以是 git 协议、HTTP/HTTPS 或者 SSH 协议的资源地址。
### 比较某个文件和远程分支上的区别
```sh
git diff local_branch remote_branch file_path
列出已删除的文件(并恢复)
从版本库历史中寻找特定代码
git rev-list --all | (
while read revision; do
git grep -F 'Your search string' $revision
done
)
应用不相关的 git 仓库中的 patch
首先将那个不相关的版本库作为一个远程版本库添加进来,并 fetch 其改动,然后 cherry-pick 你需要的那条提交记录。
设置一个新的 master 分支
修改特定的 commit
这种情况下,你可以使用 git rebase,例如,你想要修改 bbc643cd commit,运行下面的命令:
git rebase bbc643cd^ --interactive
在默认的编辑器中选择并修改你期望修改的,然后保存修改并输入:
git add
<
filepattern
>
现在你就可以使用
git commit --amend
来修改 commit,之后使用
git rebase --continue
返回之前最新的 commit。
ignore 已存在在代码库中文件的后续改动
git update-index --assume-unchanged
从不相干的 repo 中提取 commit
git --git-dir=SOME_REPO/.git format-patch -k -1 --stdout | git am -3 -k
这行命令首先从仓库 SOME_REPO 中提取 patch 并输出到 stdout,在使用 git am 命令在当前 repo 中应用 commit。
发布 dist 到 GitHub pages
在 master 分支构建 dist 并将其加入版本控制(不喜欢的话也可以开一个 orphan 分支):
git add dist # 将 dist 目录加入版本控制库,如已忽略可以 git add -f
git commit -m "Initial dist subtree commit" # 提交
git subtree push --prefix dist origin gh-pages # 使用 subtree 命令单独将 dist 目录发布到一个分支
执行 git 命令的时候忽略所有 hook
以忽略 pre-push hook 为例:
git push --no-verify
创建远程仓库
git init --bare
git remote add origin GIT_REPO_ADDR
git push -u origin master
使用 git 追踪错误
主要使用到的是 git blame 和 git bisec 命令:https://git-scm.com/book/zh/v2/Git-%E5%B7%A5%E5%85%B7-%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8-Git-%E8%B0%83%E8%AF%95
删除远程所有已合并近 master 的分支
git push origin --delete $(git branch --merged origin/master -r | grep -v master | grep origin | cut -d/ -f2-)
显示树状 git log
git log --oneline --graph
显示某一个文件的变更记录
git log -p [filename]
显示文件某几行的变更记录
git log -L [start-line],[end-line]:[filename]
显示没有合并进 master 的变更
git log --no-merges master
显示其它分支某个文件的内容
git show [branch-name]:[filename]
计算 git 项目总行数
git ls-files | xargs cat | wc -l
列出每个文件的行数:
git ls-files | xargs wc -l
pull/push 设置不同的 remote
git 1.8.3 添加了“三角关系”的支持,可以通过 branch.[branch name].pushremote 将某个分支的 pull 和 push 目标设置为不同的 remote。例如:
$ git checkout master
$ git config branch.master.remote upstream
$ git config branch.master.pushRemote origin
$ cat .git/config
[branch "master"]
merge = refs/heads/master
remote = upstream
pushRemote = origin
可以达到 master 分支每次 pull 都是从公共上游 upstream 获取更新,而 push 则是指向自己 fork 的 origin,这是一个比较搭配 GitHub flow 的使用方式。
参考链接 & 推荐阅读
- 12 个 git 实战建议和技巧
- How to undo (almost) anything with Git
- 《Pro git》在线中文版
- 常用 Git 命令清单--阮一峰
- 19 Tips For Everyday Git Use
- Different default remote (tracking branch) for git pull and git push